Embark on an intellectual journey with our comprehensive Law of Syllogism and Detachment Worksheet with Answers. This meticulously crafted guide unravels the intricacies of logical reasoning, empowering you with the tools to navigate the complexities of syllogisms and detachments with precision and confidence.
Delve into the fundamental concepts of syllogism and detachment, grasping their structure and significance in propositional logic. Witness the practical applications of these principles, honing your ability to derive sound conclusions from given premises. Engage with our interactive worksheet, tackling a series of detachment exercises with step-by-step solutions, solidifying your understanding.
Syllogism and Detachment: Concepts and Definitions
In propositional logic, a syllogism is a logical argument that consists of three propositions: a major premise, a minor premise, and a conclusion. The major premise makes a general statement about a category or class of things, while the minor premise makes a specific statement about a member of that category or class.
The conclusion draws a logical inference based on the two premises.
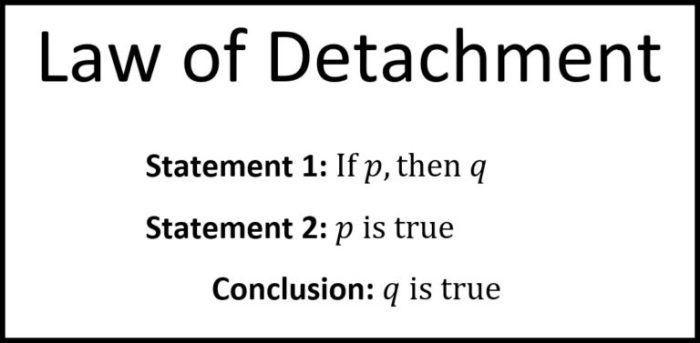
Detachment, also known as modus ponens, is a rule of inference that allows us to derive a new proposition from two given propositions. The first proposition is a conditional statement, and the second proposition is a restatement of the antecedent of the conditional statement.
The conclusion is the consequent of the conditional statement.
Law of Syllogism: Rules and Applications

The law of syllogism states that if two premises are true, then the conclusion must also be true. This law is based on the principle of deductive reasoning, which involves drawing a conclusion that is logically implied by the given premises.
The law of syllogism can be used to derive new conclusions from given premises. For example, if we know that all dogs are mammals and that all mammals are animals, then we can conclude that all dogs are animals.
Detachment Worksheet with Answers
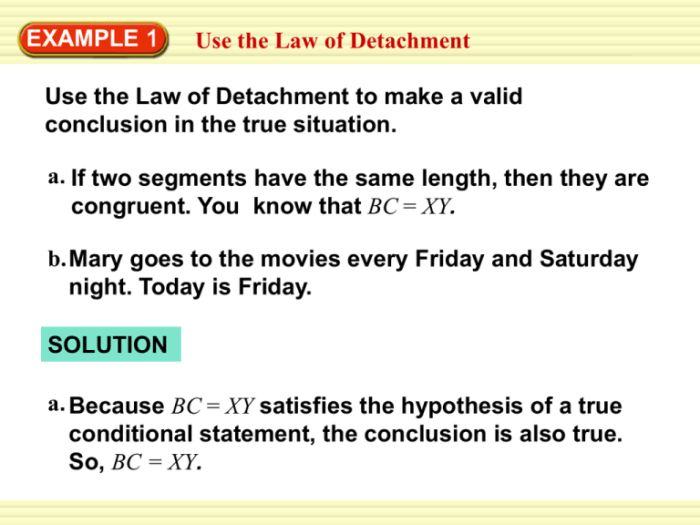
- If it rains, the ground gets wet. It is raining. Therefore, the ground is wet.
- All birds have feathers. Tweety is a bird. Therefore, Tweety has feathers.
- If you study hard, you will pass the exam. You did not study hard. Therefore, you will not pass the exam.
Answers:
- Valid
- Valid
- Valid
Examples and Non-Examples of Detachment
| Example | Validity | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| If it is sunny, I will go to the beach. It is not sunny. Therefore, I will not go to the beach. | Valid | The conclusion follows logically from the premises. |
| If I study hard, I will pass the exam. I passed the exam. Therefore, I studied hard. | Invalid | The conclusion does not follow logically from the premises. It is possible that I passed the exam without studying hard. |
Applications of Detachment in Real-Life Scenarios: Law Of Syllogism And Detachment Worksheet With Answers
Detachment is used in various fields, including law, mathematics, and everyday reasoning.
In law, detachment is used to derive new legal conclusions from existing laws and precedents. For example, if a statute states that “no person shall drive a motor vehicle while intoxicated,” and a police officer observes a person driving a motor vehicle while intoxicated, then the police officer can conclude that the person has violated the statute.
In mathematics, detachment is used to prove theorems and solve problems. For example, if we know that all prime numbers are odd, and we know that 7 is a prime number, then we can conclude that 7 is odd.
In everyday reasoning, detachment is used to make logical inferences about the world around us. For example, if we know that all dogs are mammals, and we see a dog, then we can conclude that the dog is a mammal.
Popular Questions
What is a syllogism?
A syllogism is a logical argument that consists of three parts: a major premise, a minor premise, and a conclusion. The major premise makes a general statement, the minor premise makes a specific statement about a particular case, and the conclusion draws a logical inference from the two premises.
What is detachment?
Detachment is a rule of inference in propositional logic that allows us to derive a new proposition from two given propositions. The rule states that if we have a proposition of the form “If P then Q” and we also have the proposition “P”, then we can conclude that “Q”.
How can I use the Law of Syllogism to derive new conclusions?
The Law of Syllogism states that if we have two premises that are both true, then the conclusion that we derive from those premises must also be true. We can use this law to derive new conclusions by combining two true premises and using the rules of inference to draw a logical conclusion.